PHARMACY
Tuesday, April 07, 2020
MICROSPHERES
MICROSPHERES
Microspheres are solid spherical free flowing powder. They are solid and hollow. The production of microsphere from natural, synthetic polymeric materials or inorganic materials which are mostly biodegradable in nature. Particles diameters in micrometre range from 1 to 1000 μm. Microsphere is also known as microparticles, spherical microparticles.
POLYMERS USED IN MICROSPHERES
Synthetic polymers
Lactides, glycolides, copolymers, polyalkyl cyanoacrylates, polyanhidrides, PMMA, Acrolein, Epoxy polymers
Natural polymers
Albumins, Starch agarose, Carrageenan, Chitosan, Gelatin, Collagen, Poly dextran, Poly starch, DEAE cellulose.
Types of Microsphere:
1.Radioactive microspheres: They are delivered very high radiation doses to the site of action without affecting the surrounding tissues and cells. Three type of emitters: Alpha, beta and gamma.
2. Bioadhesive microspheres: Bioadhesion is basically capability of material to adhere to tissues for the extended time period. They increase the penetration of active ingredients.
3. Floating microspheres: They are gastro retententive systems, low density and have sufficient capability to float over the surface of gastric content . They released the drug slowly at desired rate.
4. Mucoadhesive polymeric microspheres: It directly contacts with the mucous layer covering the mucosal epithelial surface it increases the residence time.
ADVANTAGES:
1. Increases in Solubility ,due to Reduced Size.
2. Patient compliance.
3. Less dose, less toxicity
4. Dosing frequency is limited.
5. GIT Protection from effects of drugs.
6. Taste and odor masking properties.
7. Increase bioavailability.
8. Improves powder flow
9. Incompatible material separation.
10. Conversion of liquid to solid is easy.
DISADVANTAGES:
1. Cost is higher than standard formulations.
2. Less reproducibility.
3. Change in conditions like temperature, pressure, ph may affect the system.
4. Degradation or deterioration of product due to environmental changes.
APPLICATIONS:
1. Delivery of Vaccines.
2. Drug targeting to particular site.
3. Chemo mobilization
4. Controlled drug release.
5. Microencapsulated activated charcoal
6. Encapsulation of microbial cells.
7. Targeting by Using Micro Particulate Carriers
8. Direct couplings.
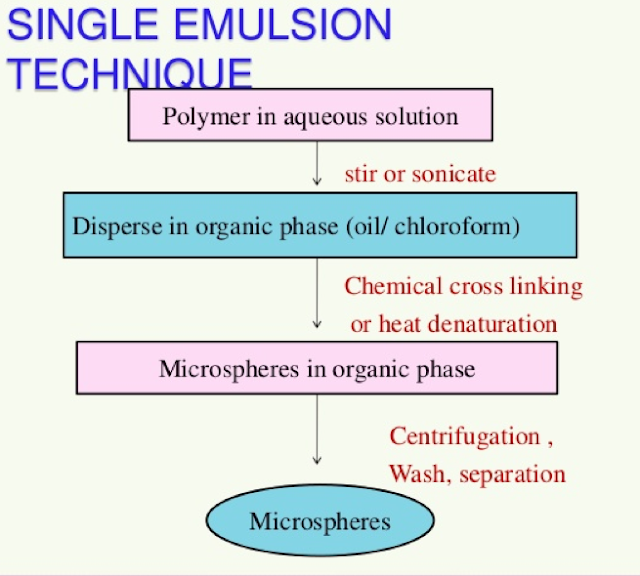
Methods of preparation
1. Solvent extraction: Dispersion of drug in organic solvent, Now add polymer in organic solvent, removal of organic phase by extraction of water and microspheres are formed.
2.Double emulsion technique: Drug is dissolved in aqueous solution, sonicate the solution for dispersing it in organic phase properly.first emulsion is formed (W/O) now add aq. Solution of PVA,Formation of multiple emulsion Now again add large aqueous phase to it and microspheres are formed in the solution.
3.Solvent evaporation: Core material dispersed in polymer solution and continue stirring core material disperse in liquid Manufacturing vehicle phase, Slightly heat up and solvent is going to evaporate and Microsphere are formed.
4.Phase sapartion /coaservation technique: Drug is dispersed or dissolved in the aqueous or organic solution of polymer.After induction of phase separation polymer rich globules are solidify and microspheres are formed.
5. Spray drying: First of all dissolve the polymer into organic phase.When the drug is dispersed in solution. Atomized in a stream of air.Now Small droplets are formed and solvent is evaporated.Finally the miocrospheres are prepared.
Conclusion:
Microspheres drug delivery system forms the micro size particles which are delivered in the target areas of the body, As their Reduced size, chances of solubility is increased and finally it positively response to the increase in bioavailability of the drug.
Video links: https://youtu.be/67FRYQ7iH90.